Overview
In the standard setup of the Ardupilot Mega (APM) for Rovers you would deploy a conventional RC for manual control: the RC receiver feeds the input channels of the APM with PWM signals for Rover movement and for executing special functions such as switching flight modes.
If you replace the conventional remote control receiver with a PiKoder receiver – either WLAN- (PiKoder/SSC wRX or Bluetooth -communication (PiKoder/SSC RX), then the Ardupilot can be controlled via an Android based smartphone or tablet using the remote control apps udpRC or respectively btRC.
Setting up the rover
First, the APM is loaded with the Mission Planner with the ROVER configuration; a further adjustment of the parameters was not necessary in my case.
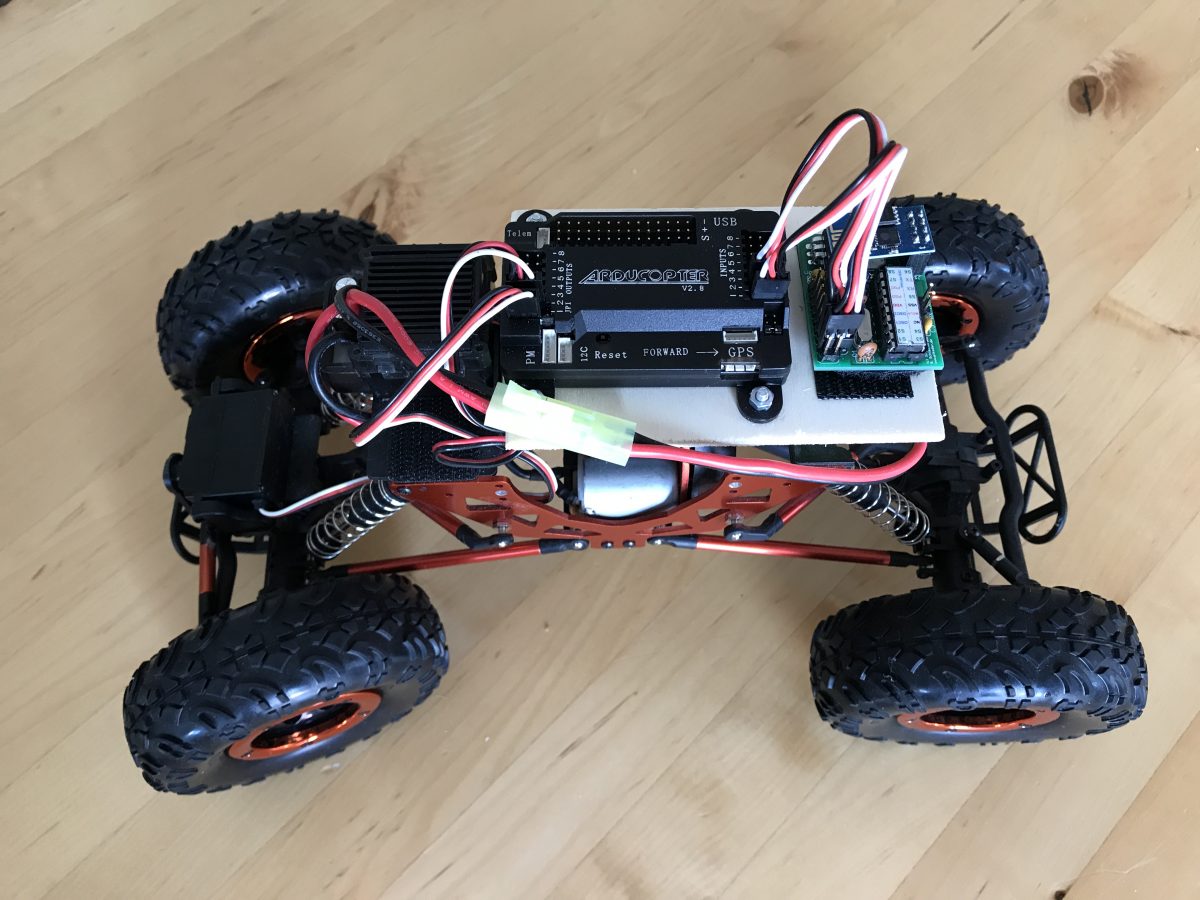
The following image shows the very simple hardware setup.
The PiKoder – channel 1 is connected to the APM input 1 (steering) and the PiKoder – channel 2 to the input 3 (throttle). The standard rover wiring is used at the output side (steering servo on channel 1, ESC with BEC on channel 3). In this configuration, the Ardupilot takes over the power supply of the receiver.
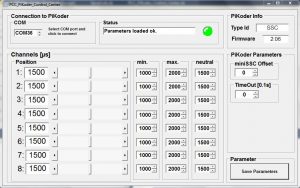
The Ardupilot does not respond to PWM signals that are below or exceeding the typical range of approx. 1,000 – 2,000 µs. Therefore, the minimum and maximum values of the pulse values of the PiKoder/SSC have to be adjusted, as shown in the following figure.
For this purpose, the PiKoder Control Center (PCC) is used as described in the User’s Manual for the PiKoder/SSC wRX.
This completes the set up; the function of the apps is described in the user manuals.